Tutorial
- How to import LabChart’s HRV report file (
.txt) into a tidy tibble with 1 subject per rows.
Export HRV report file
After you’ve analysed the HRV data in LabChart, follow these steps to export HRV report:
Go to menu HRV -> Export Report... -> save file as .txt
Open that file, it should look like this:
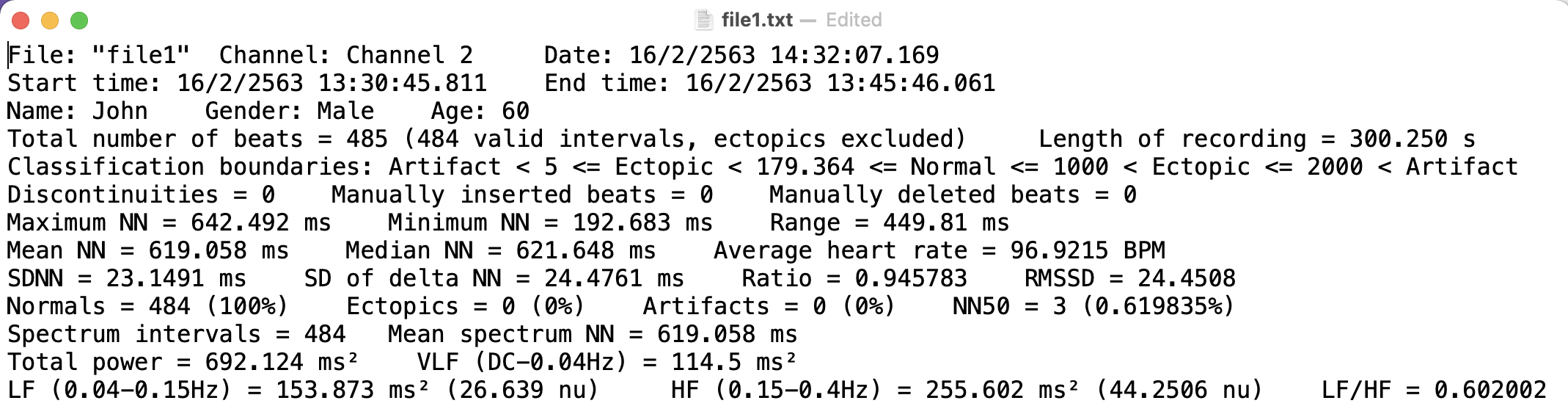
As you can see, the text file is slightly formatted and store data in key-value pairs (mostly).
How to transform it so that a data analysis can be performed?
To process this data for further analysis, one approach is to convert it to a table-like data structure which, in R, is a data frame (or tibble). The design of this data frame should be tidy, meaning column names are variables, and each rows represent a single subject. (As in this example, it should be converted to a 1 row data frame.)
It takes time and effort to manually transforms this into a table which can be even harder when the number of subject grows.
That’s why I’ve build this package!
Read HRV report file
read_HRV_reports() read and transform LabChart’s HRV report file (.txt) to a tidy tibble.
The first argument (file) is a path to either single HRV report file or folder containing multiple HRV report file, the latter case should be more useful to you.
# Path to a folder containing example HRV report text files
path_hrv <- labChartHRV_example("HRV")
path_hrv
#> [1] "/home/runner/work/_temp/Library/labChartHRV/extdata/HRV"There are 4 HRV report .txt files in this folder.
dir(path_hrv)
#> [1] "file1.txt" "file2.txt" "file3.txt" "file4.txt"Now, just supply the path to the folder to import it.
# Read In
hrv_tbl <- read_HRV_reports(path_hrv)
hrv_tbl
#> # A tibble: 4 × 41
#> doc_id File_LabChart Channel Date Start_time End_time Name Gender Age
#> <chr> <chr> <fct> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <fct> <int>
#> 1 file1.txt file1 Channel 2 16/2… 16/2/2563… 16/2/25… John Male 60
#> 2 file2.txt file2 Channel 2 26/3… 26/3/2563… 26/3/25… Max Male 56
#> 3 file3.txt file3 Channel 2 19/8… 19/8/2563… 19/8/25… Mary Female 65
#> 4 file4.txt file4 Channel 2 10/9… 19/10/256… 19/10/2… Tom Female 63
#> # … with 32 more variables: Beats_tot <dbl>, Rec_length <dbl>,
#> # Class_bound <chr>, Discontinuities <dbl>, Beats_inserted <dbl>,
#> # Beats_deleted <dbl>, NN_max <dbl>, NN_min <dbl>, NN_range <dbl>,
#> # NN_mean <dbl>, NN_median <dbl>, HR_avg <dbl>, SDNN <dbl>, SD_del_NN <dbl>,
#> # RMSSD <dbl>, Normals_count <dbl>, Ectopics_count <dbl>,
#> # Artifacts_count <dbl>, NN50_count <dbl>, NN50_percent <dbl>,
#> # Spec_intv <dbl>, Spec_mean_NN <dbl>, Power_tot <dbl>, VLF_freq <chr>, …(Note: Internally read_HRV_reports() use readtext::readtext() to read textual data. I’ve set the text encoding to UTF-16LE. If you found that the output looks abnormal try changing text encoding via argument encoding.)
hrv_tbl has 41 columns and 4 rows. Column names correspond to each fields of the HRV report, and each rows correspond to each HRV report files.
# Column Names
names(hrv_tbl)
#> [1] "doc_id" "File_LabChart" "Channel" "Date"
#> [5] "Start_time" "End_time" "Name" "Gender"
#> [9] "Age" "Beats_tot" "Rec_length" "Class_bound"
#> [13] "Discontinuities" "Beats_inserted" "Beats_deleted" "NN_max"
#> [17] "NN_min" "NN_range" "NN_mean" "NN_median"
#> [21] "HR_avg" "SDNN" "SD_del_NN" "RMSSD"
#> [25] "Normals_count" "Ectopics_count" "Artifacts_count" "NN50_count"
#> [29] "NN50_percent" "Spec_intv" "Spec_mean_NN" "Power_tot"
#> [33] "VLF_freq" "VLF" "LF_freq" "LF"
#> [37] "LF_nu" "HF_freq" "HF" "HF_nu"
#> [41] "LF_HF"The description of each columns is stored in HRV_vars_desc data frame.
HRV_vars_desc
#> # A tibble: 41 × 2
#> variable description
#> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 doc_id File name of the input HRV reports
#> 2 File_LabChart LabChart file name
#> 3 Channel Channel
#> 4 Date Date
#> 5 Start_time Start time
#> 6 End_time End time
#> 7 Name Name
#> 8 Gender Gender
#> 9 Age Age
#> 10 Beats_tot Total number of beats
#> # … with 31 more rowsParse HRV report
parse_HRV_reports() is a lower-level function that parse HRV report from character vector to a data frame.
Read Manually
First, you need to read HRV report in to character vector using any text reading engine of your choice.
# Path to an HRV report text file
path_hrv1 <- labChartHRV_example("HRV/file1.txt")
# Read into character vector, I use `{readtext}`
hrv_chr <- readtext::readtext(path_hrv1,
encoding = "UTF-16LE")$text
# For nice printing
glue::as_glue(hrv_chr)
#> File: "file1" Channel: Channel 2 Date: 16/2/2563 14:32:07.169
#> Start time: 16/2/2563 13:30:45.811 End time: 16/2/2563 13:45:46.061
#> Name: John Gender: Male Age: 60
#> Total number of beats = 485 (484 valid intervals, ectopics excluded) Length of recording = 300.250 s
#> Classification boundaries: Artifact < 5 <= Ectopic < 179.364 <= Normal <= 1000 < Ectopic <= 2000 < Artifact
#> Discontinuities = 0 Manually inserted beats = 0 Manually deleted beats = 0
#> Maximum NN = 642.492 ms Minimum NN = 192.683 ms Range = 449.81 ms
#> Mean NN = 619.058 ms Median NN = 621.648 ms Average heart rate = 96.9215 BPM
#> SDNN = 23.1491 ms SD of delta NN = 24.4761 ms Ratio = 0.945783 RMSSD = 24.4508
#> Normals = 484 (100%) Ectopics = 0 (0%) Artifacts = 0 (0%) NN50 = 3 (0.619835%)
#> Spectrum intervals = 484 Mean spectrum NN = 619.058 ms
#> Total power = 692.124 ms² VLF (DC-0.04Hz) = 114.5 ms²
#> LF (0.04-0.15Hz) = 153.873 ms² (26.639 nu) HF (0.15-0.4Hz) = 255.602 ms² (44.2506 nu) LF/HF = 0.602002Parse to Data Frame
Now parse the character vector to a data frame.
parse_HRV_reports(hrv_chr)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 40
#> File_LabChart Channel Date Start_time End_time Name Gender Age Beats_tot
#> <chr> <fct> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <fct> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 file1 Channel 2 16/2… 16/2/2563… 16/2/25… John Male 60 485
#> # … with 31 more variables: Rec_length <dbl>, Class_bound <chr>,
#> # Discontinuities <dbl>, Beats_inserted <dbl>, Beats_deleted <dbl>,
#> # NN_max <dbl>, NN_min <dbl>, NN_range <dbl>, NN_mean <dbl>, NN_median <dbl>,
#> # HR_avg <dbl>, SDNN <dbl>, SD_del_NN <dbl>, RMSSD <dbl>,
#> # Normals_count <dbl>, Ectopics_count <dbl>, Artifacts_count <dbl>,
#> # NN50_count <dbl>, NN50_percent <dbl>, Spec_intv <dbl>, Spec_mean_NN <dbl>,
#> # Power_tot <dbl>, VLF_freq <chr>, VLF <dbl>, LF_freq <chr>, LF <dbl>, …Since I’ve import only 1 HRV report into a character vector of length 1, the resulting data frame has only 1 row.
However, you can supply HRV report character vector which has > 1 length, and the resulting data frame would have multiple rows corresponding to each HRV reports.
Selection Helper
labChartHRV comes with a helper for select HRV time-and frequency-domain variables.
HRV_vars_domain is a list with 2 elements:
time: contains character vector of time-domain variables.freq: contains character vector of frequency-domain variables.
For example
vars <- HRV_vars_domain
str(vars)
#> List of 2
#> $ time: chr [1:6] "SDNN" "SD_del_NN" "RMSSD" "Normals_count" ...
#> $ freq: chr [1:10] "Power_tot" "VLF_freq" "VLF" "LF_freq" ...Select HRV time-domain variables.
hrv_tbl %>%
select(Name, vars$time)
#> # A tibble: 4 × 7
#> Name SDNN SD_del_NN RMSSD Normals_count NN50_count NN50_percent
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 John 23.1 24.5 24.5 484 3 0.620
#> 2 Max 31.0 14.2 14.2 400 2 0.5
#> 3 Mary 17.1 5.58 5.58 420 0 0
#> 4 Tom 22.2 6.20 6.19 434 1 0.230Last updated: 2022-06-08
